In January last year, Reuters polled 1,000 oil market experts who basically agreed that oil would remain anchored in the $65-$70/bbl range through 2023. Only 3% of these experts thought that oil might rise to $90/bbl or more in 2020. I posted my analysis at this link: Market Fundamentals and Forecasting Groupthink. Later that year I published my own analysis, “Next Move in Oil Prices: $5-$10 Lower,” concluding that, …oil price will likely see another leg down… with Brent falling toward high $40s and WTI toward low $40s. Continue reading
Tag Archives: Oil price

The oil price shock: has it arrived?
Experts seldom expect surprises. In spite of the ever deepening economic and political uncertainties gripping most oil producing and oil consuming regions, most market experts surveyed last year predicted that oil price would fluctuate between $65 and $70 through 2023.
That forecast assumes that nothing unforeseen would happen over the next five years. Such an assumption, to put it politely, is unjustified and the list of reasons is long and complex, and it can be neither ignored nor wished away. Over the recent months I’d written a handful of articles on the subject of the ‘coming oil price shock.’ Here are the last three: Continue reading
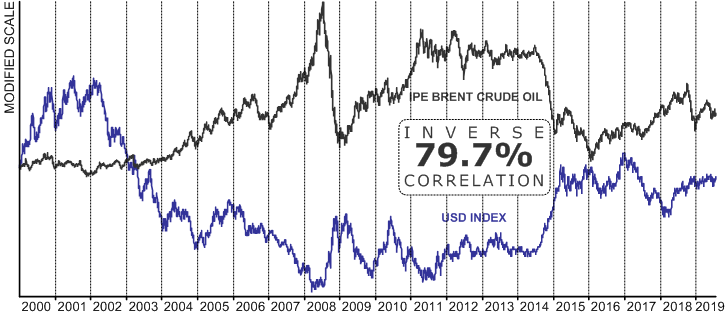
Failure of price forecasting: the unit of account conundrum
In addition to the better understood challenges of market analysis, like access to timely and accurate data, there is another – rather massive, but usually completely ignored – problem that renders forecasting largely an exercise in futility.
Over the years I’ve written quite a bit on the unreliable nature of price forecasts based on the analysis of market supply and demand . Most recently, in “Market fundamentals, forecasting and the groupthink effect,” I discussed the problem of data quality as well as the very real problem of groupthink among leading analysts, providing an example of a staggeringly wrong oil price forecast they produced. Some of the very same experts later produced this gem: Continue reading
The coming oil price shock: could the crisis in Venezuela trigger an energy crisis?
Measured by historical standards, the price of oil has been extremely volatile in recent years. From over $114 per barrel in the summer of 2014 it collapsed more than 75% in only 18 months’ time. Then it tripled to $86/bbl in October 2018, only to drop by 40% to $52/bbl two months later. The question is, why is the oil price so very volatile? Is the market foreshadowing greater disruptions in the future? A closer look into oil supply and demand fundamentals suggests that a great crisis could be in the making – possibly with alarming repercussions.
The looming oil shortage
In 2012 a report produced by the UK Ministry of Defence predicted that oil prices would rise significantly out to 2040, and by “significantly,” they meant to $500 per barrel. From today’s perspective, this may seem farfetched. However, we should not dismiss UKMOD’s warning lightly. This could turn out to be the most important development facing humanity for decades to come. Continue reading

How we navigated the oil price roller coaster
Extreme price events are far and away the greatest source of external risk facing oil and gas producers and other energy-dependent companies. Frequency and severity of such events has been increasing dramatically since about 2005/2006 causing ocasionally severe pain for many industry participants.
Case in point was the 70% oil price collapse through 2014 and 2015, from over $100 to below $30 per barrel. In the aftermath of this decline, U.S. mining industry – which includes oil and gas producers – reported losses of $227 billion, wiping out eight previous years’ worth of profits as the following chart shows: Continue reading
Is an epic energy crunch in the making?
Last year I published a report with the (justifiably) bombastic title, “$500 per barrel: could oil price rise tenfold?” One of my central claims was that producing oil requires investment of real capital including materials, equipment and highly skilled labor, and that, “as more and more resources are required to generate the same amount of liquid fuels, energy production is becoming ever more expensive to society in real terms.” Thus, as it becomes more expensive in real terms (as the deteriorating EROEI figures indicate), the fact that energy has recently become cheaper in nominal (dollar) terms can only be a temporary abberation. EROEI stands for energy return on energy invested; in the early 1900s, we obtained 100 barrels euqivalent of oil per barrel invested (EROEI of 100 to 1); today we are at about 15 to 1 globally and at 11 to 1 in the USA. Continue reading
Saudis to unveil the big secret? Not likely.
Over at OilPrice.com Nick Cunningham wrote that Saudi Arabia might finally reveal one of its closest kept secrets as they prepare to sell some 5% of its oil monopoly, Saudi Aramco, to the public. The Saudis and their Wall Street bankers expect Aramco to be valued at $2 to $3 trillion, which would generate north of $100 billion for the Saudis and massive underwriting fees for Wall Street Banks.
Since both the Saudis and Wall Street hope for the highest possible valuation for Aramco, we should not expect that they’ll “unveil” anything less than the rosiest plausible figure for their oil reserves. Continue reading
5/5: $500 oil and how to manage the looming uncertainty and risk
Let us recap what we covered in parts 1, 2, 3 and 4 of this report. In spite of the low price of oil (just below $50 at the time of this writing) and predominantly bearish market sentiment, the “big picture” suggests that we are facing a grave energy predicament. Petroleum producing countries, especially members of OPEC, have been vastly overstating their oil reserves. Production of oil from conventional sources is in an irreversible decline. Over the next 15 years, the EIA projected that production will fall over 40% short of demand. New drilling technologies, and this includes fracking, are unlikely to impact this shortfall in a meaningful way. These conditions have led the UK’s Ministry of Defence to predict in 2012 that oil price could rise to as high as $500 per barrel over the next three decades, causing crises of unforeseeable proportions. For the oil market participants, the trillion dollar question is how to cope with the looming uncertainty and risks. Continue reading
4/5: Sources and quality of oil market information
This posting is part 4 in the 5-part series on the future energy crisis we are likely facing. Here are parts one, two, and three. My research to try and establish facts about oil supply and demand led to many dead-ends where you must take the information at face value and hope that it is true. For example, we’ve all heard (again) about tanker-fulls of unsold crude oil floating around the world, but ultimately, this information was based on hearsay. For example, Bloomberg reported how oil companies are seeking supertankers to store 20 million barrels of crude oil [i] (that sounds like a lot, but it represents only a few hours’ worth of global demand). Continue reading